Trees:
Trees are non-linear data structures that represent nodes connected by edges. Each tree consists of a root node as the Parent node, and the left node and right node as Child nodes.
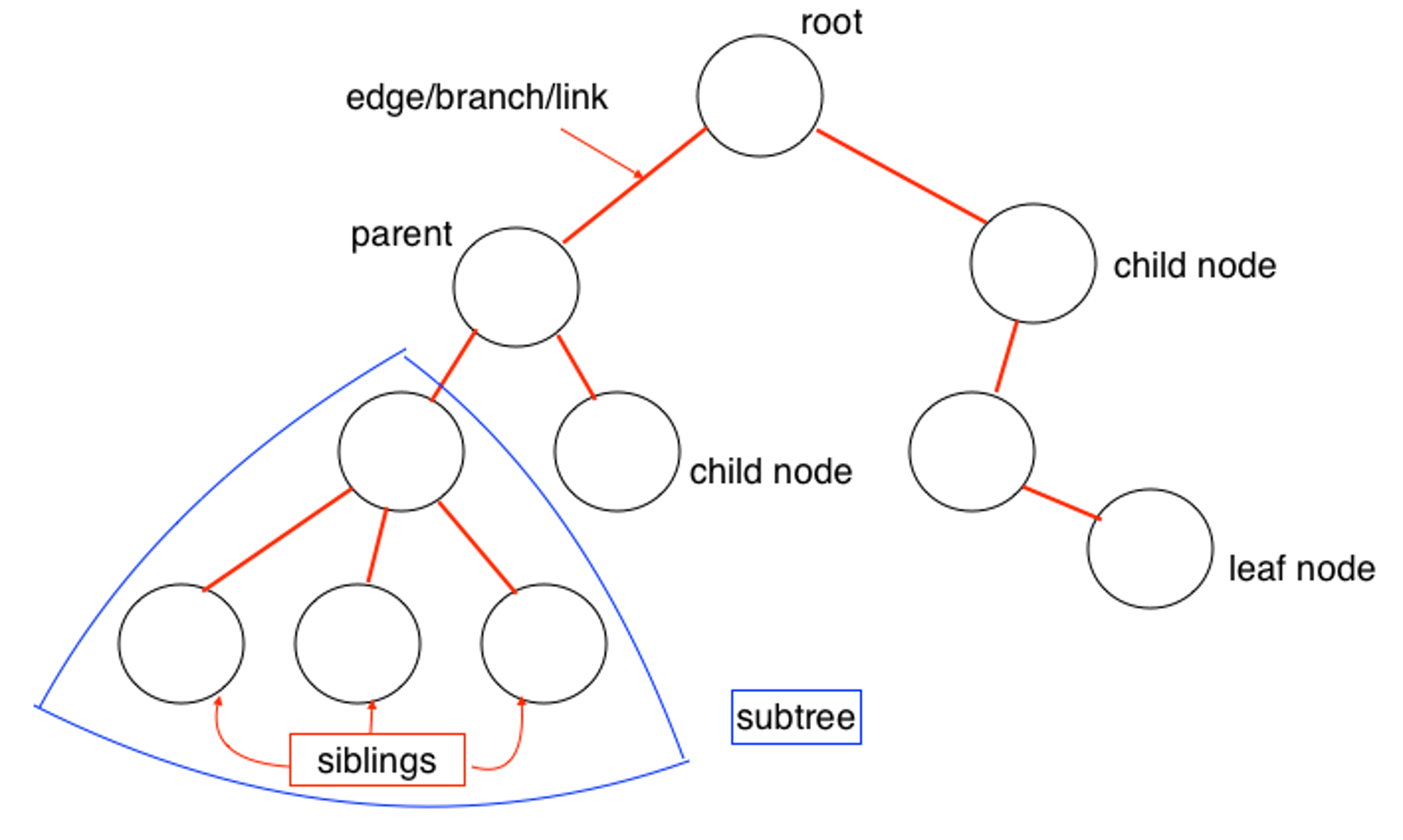
Binary tree:
A tree whose elements have at most two children is called a binary tree. Each element in a binary tree can have only two children. A node’s left child must have a value less than its parent’s value, and the node’s right child must have a value greater than its parent value.
Implementation:
Here we have created a node class and assigned a value to the node.
# node class
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
# left child
self.left = None
# right child
self.right = None
# node's value
self.data = data
# print function
def PrintTree(self):
print(self.data)
root = Node(27)
root.PrintTree()
Insertion:
The insert method compares the value of the node to the parent node and decides whether to add it as a left node or right node. Remember: if the node is greater than the parent node, it is inserted as a right node; otherwise, it’s inserted left. Finally, the PrintTree method is used to print the tree.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
def insert(self, data):
# Compare the new value with the parent node
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
# Print the tree
def PrintTree(self):
if self.left:
self.left.PrintTree()
print( self.data),
if self.right:
self.right.PrintTree()
# Use the insert method to add nodes
root = Node(27)
root.insert(14)
root.insert(35)
root.insert(31)
root.insert(10)
root.insert(19)
root.PrintTree()
Searching :
While searching for a value in the tree, we need to traverse the node from left to right and with a parent.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
# Insert method to create nodes
def insert(self, data):
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
# findval method to compare the value with nodes
def findval(self, lkpval):
if lkpval < self.data:
if self.left is None:
return str(lkpval)+" is not Found"
return self.left.findval(lkpval)
elif lkpval > self.data:
if self.right is None:
return str(lkpval)+" is not Found"
return self.right.findval(lkpval)
else:
return str(self.data) + " is found"
# Print the tree
def PrintTree(self):
if self.left:
self.left.PrintTree()
print(self.data),
if self.right:
self.right.PrintTree()
root = Node(27)
root.insert(14)
root.insert(35)
root.insert(31)
root.insert(10)
root.insert(19)
print(root.findval(7))
print(root.findval(14))