stack and Queue (visualization):
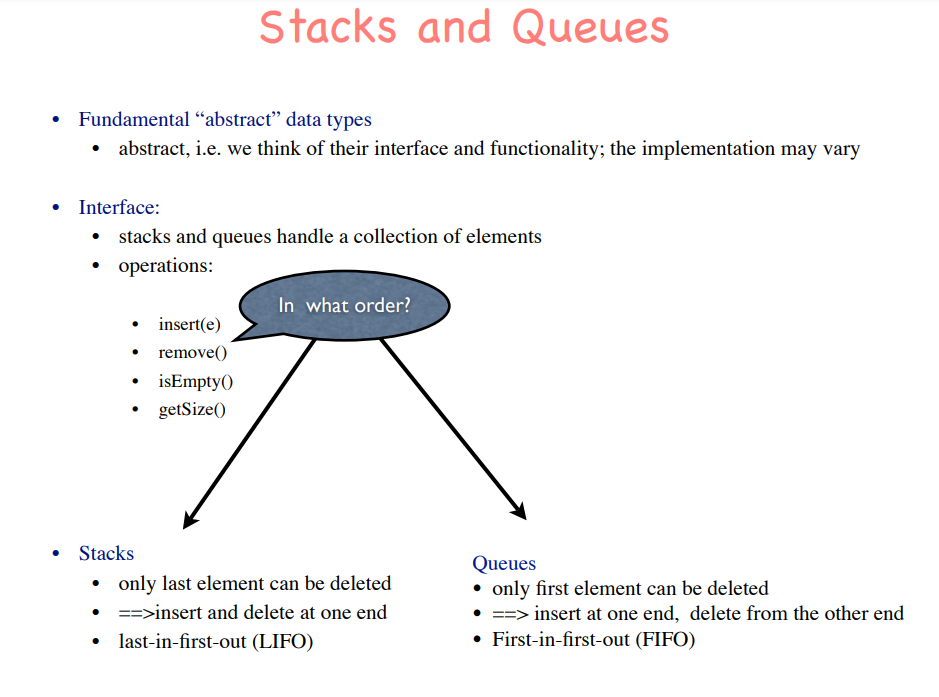
Structure :
stack :
In computer science, a stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection of elements, with two main principal operations:
Push, which adds an element to the collection, and Pop, which removes the most recently added element that was not yet removed. The order in which elements come off a stack gives rise to its alternative name, LIFO (last in, first out). Additionally, a peek operation may give access to the top without modifying the stack. The name “stack” for this type of structure comes from the analogy to a set of physical items stacked on top of each other. This structure makes it easy to take an item off the top of the stack, while getting to an item deeper in the stack may require taking off multiple other items first.
Considered as a linear data structure, or more abstractly a sequential collection, the push and pop operations occur only at one end of the structure, referred to as the top of the stack. This data structure makes it possible to implement a stack as a singly linked list and a pointer to the top element. A stack may be implemented to have a bounded capacity. If the stack is full and does not contain enough space to accept an entity to be pushed, the stack is then considered to be in an overflow state. The pop operation removes an item from the top of the stack.
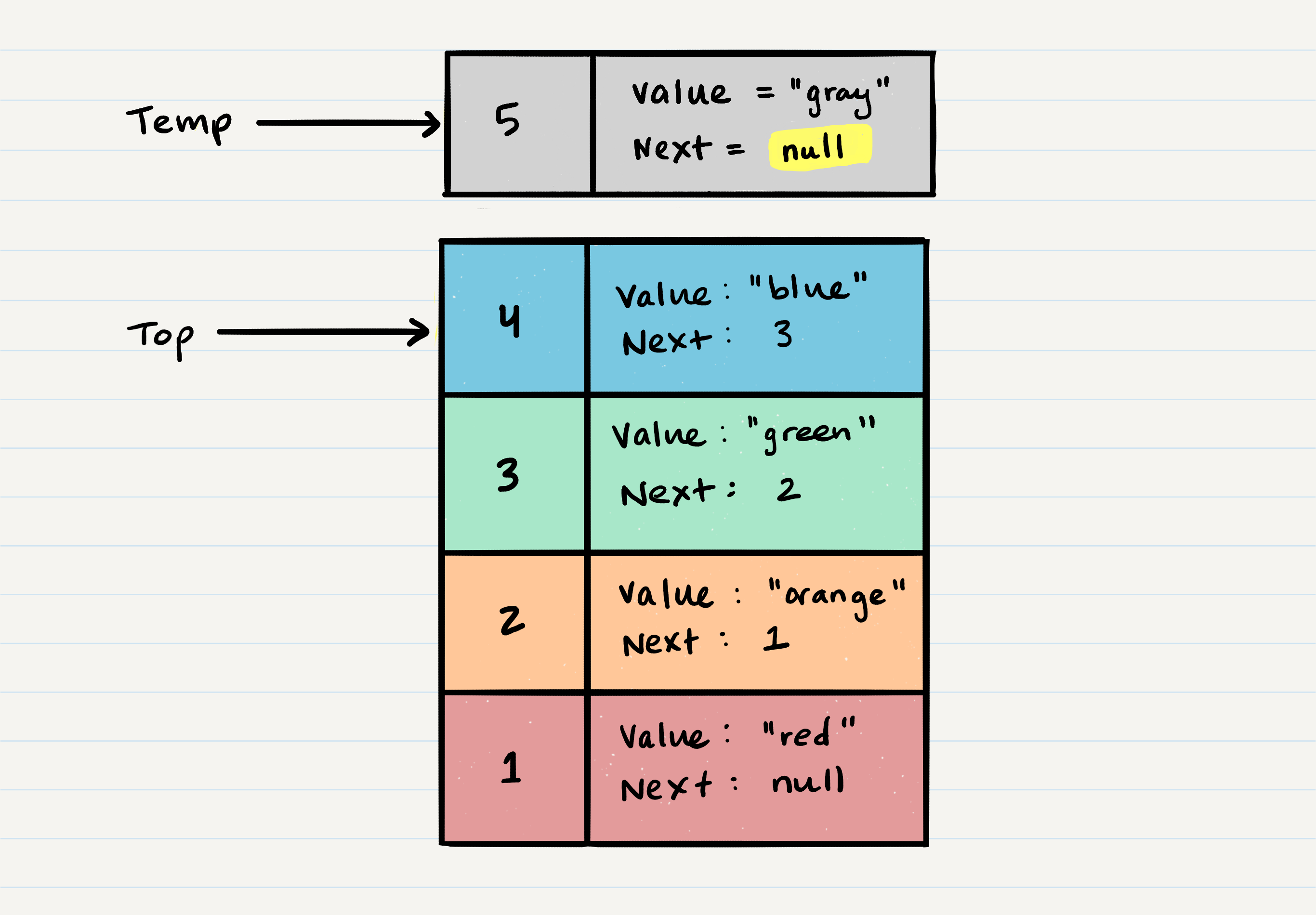
ALGORITHM pop()
// INPUT <-- No input
// OUTPUT <-- value of top Node in stack
// EXCEPTION if stack is empty
Node temp <-- top
top <-- top.next
temp.next <-- null
return temp.value
Queue:
In computer science, a queue is a collection of entities that are maintained in a sequence and can be modified by the addition of entities at one end of the sequence and the removal of entities from the other end of the sequence. By convention, the end of the sequence at which elements are added is called the back, tail, or rear of the queue, and the end at which elements are removed is called the head or front of the queue, analogously to the words used when people line up to wait for goods or services.
The operation of adding an element to the rear of the queue is known as enqueue, and the operation of removing an element from the front is known as dequeue. Other operations may also be allowed, often including a peek or front operation that returns the value of the next element to be dequeued without dequeuing it.
The operations of a queue make it a first-in-first-out (FIFO) data structure. In a FIFO data structure, the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed. This is equivalent to the requirement that once a new element is added, all elements that were added before have to be removed before the new element can be removed. A queue is an example of a linear data structure, or more abstractly a sequential collection. Queues are common in computer programs, where they are implemented as data structures coupled with access routines, as an abstract data structure or in object-oriented languages as classes. Common implementations are circular buffers and linked lists.
Queues provide services in computer science, transport, and operations research where various entities such as data, objects, persons, or events are stored and held to be processed later. In these contexts, the queue performs the function of a buffer. Another usage of queues is in the implementation of breadth-first search.
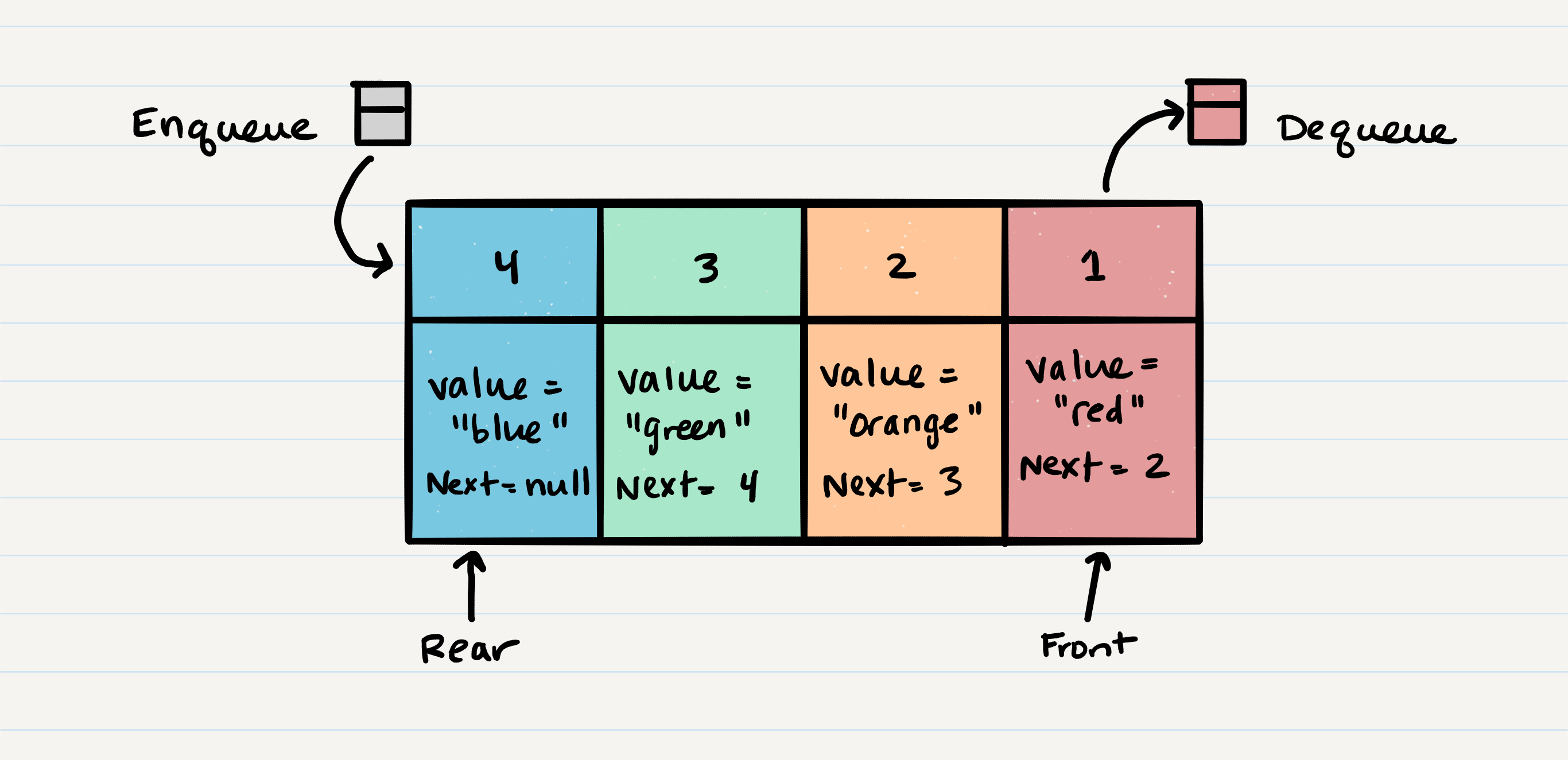
ALGORITHM dequeue()
// INPUT <-- none
// OUTPUT <-- value of the removed Node
// EXCEPTION if queue is empty
Node temp <-- front
front <-- front.next
temp.next <-- null
return temp.value
Cheats sheet
The Stack Abstract Data Type
• A stack is an abstract data type (ADT) that supports
two main methods:
- push(o): Inserts object o onto top of stack
Input: Object; Output: none
- pop(): Removes the top object of stack and
returns it; if stack is empty an error occurs
Input: none; Output: Object
• The following support methods should also be
defined:
- size(): Returns the number of objects in stack
Input: none; Output: integer
- isEmpty(): Return a boolean indicating if stack is
empty.
Input: none; Output: boolean
- top(): return the top object of the stack,
without removing it; if the stack is
empty an error occurs.
Input: none; Output: Object
this a quiz for you
write cheat sheet for the queue
Remember :
- FOUCS
- no pain no gain
- work hard
writen by OBADA ALHAWJREH.
My name is obada jaber, I’m 27 years old, I studied Mechanical engineering and i graduated from al balqa applied university, i am now a software student. OBADA ALHAWJREH.
Support or Contact:
Having trouble with Pages? Check out our : email or phone number : 0781912474 or contact support for gethub and we’ll help you sort it out. 🚑 🚑 🚑