JupyterLab
JupyterLab is a next-generation web-based user interface for Project Jupyter.
You can arrange multiple documents and activities side by side in the work area using tabs and splitters. Documents and activities integrate with each other, enabling new workflows for interactive computing, for example:
Code Consoles provide transient scratchpads for running code interactively, with full support for rich output. A code console can be linked to a notebook kernel as a computation log from the notebook, for example.
Kernel-backed documents enable code in any text file (Markdown, Python, R, LaTeX, etc.) to be run interactively in any Jupyter kernel.
Notebook cell outputs can be mirrored into their own tab, side by side with the notebook, enabling simple dashboards with interactive controls backed by a kernel.
Multiple views of documents with different editors or viewers enable live editing of documents reflected in other viewers. For example, it is easy to have live preview of Markdown, Delimiter-separated Values, or Vega/Vega-Lite documents.
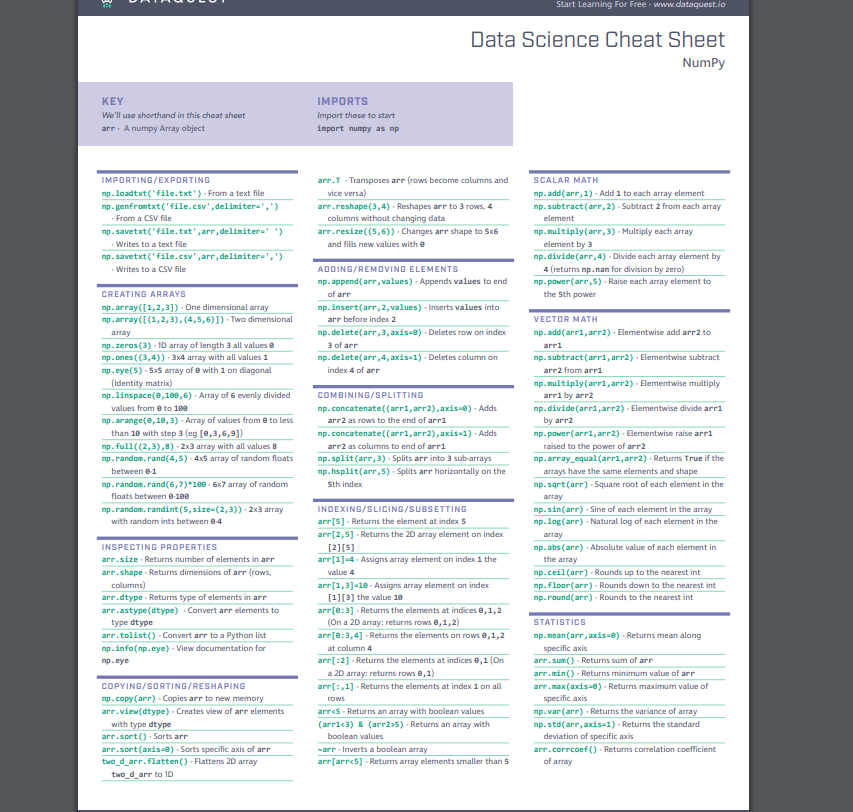
NumPy Tutorial: Data Analysis with Python:
NumPy stands for Numerical Python and is one of the most useful scientific libraries in Python programming. It provides support for large multidimensional array objects and various tools to work with them. Various other libraries like Pandas, Matplotlib, and Scikit-learn are built on top of this amazing library.
Arrays are a collection of elements/values, that can have one or more dimensions. An array of one dimension is called a Vector while having two dimensions is called a Matrix.
NumPy arrays are called ndarray or N-dimensional arrays and they store elements of the same type and size. It is known for its high-performance and provides efficient storage and data operations as arrays grow in size.