Dunder methods in Python:
Dunder or magic methods in Python are the methods having two prefix and suffix underscores in the method name. Dunder here means “Double Under (Underscores)”. These are commonly used for operator overloading. Few examples for magic methods are: __init__, __add__, __len__, __repr__ etc.
The __init__ method for initialization is invoked without any call, when an instance of a class is created, like constructors in certain other programming languages such as C++, Java, C#, PHP etc. These methods are the reason we can add two strings with ‘+’ operator without any explicit typecasting.
Here’s a simple implementation :
# declare our own string class
class String:
# magic method to initiate object
def __init__(self, string):
self.string = string
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# object creation
string1 = String('Hello')
# print object location
print(string1)
#output:
<__main__.String object at 0x7fe992215390>
#Now add __add__ method to String class :
# declare our own string class
class String:
# magic method to initiate object
def __init__(self, string):
self.string = string
# print our string object
def __repr__(self):
return 'Object: {}'.format(self.string)
def __add__(self, other):
return self.string + other
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# object creation
string1 = String('Hello')
# concatenate String object and a string
print(string1 +' Geeks')
#Output :
Hello Geeks
#If we try to add a string to it :
# declare our own string class
class String:
# magic method to initiate object
def __init__(self, string):
self.string = string
# print our string object
def __repr__(self):
return 'Object: {}'.format(self.string)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# object creation
string1 = String('Hello')
# concatenate String object and a string
print(string1 +' world')
#Output :
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'String' and 'str'
What is probability?
At the most basic level, probability seeks to answer the question, “What is the chance of an event happening?” An event is some outcome of interest. To calculate the chance of an event happening, we also need to consider all the other events that can occur. The quintessential representation of probability is the humble coin toss. In a coin toss the only events that can happen are:
- Flipping a heads
- Flipping a tails
Python Probability Distributions – Normal, Binomial, Poisson, Bernoulli:
A probability distribution is a function under probability theory and statistics- one that gives us how probable different outcomes are in an experiment. It describes events in terms of their probabilities; this is out of all possible outcomes. Let’s take the probability distribution of a fair coin toss. Here, heads take a value of X=0.5 and tails gets X=0.5 too. Two classes of such a distribution are discrete and continuous. The former represented by a probability mass function and the latter by a probability density function.
How to Implement Python Probability Distributions?:
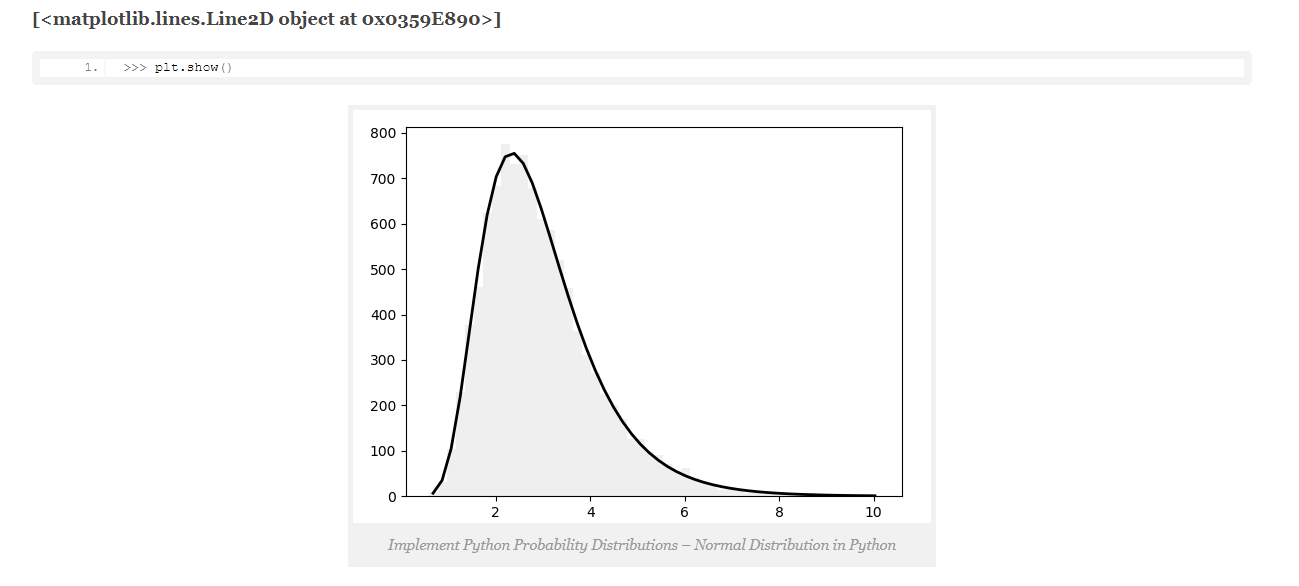
a. Normal Distribution in Python: Python normal distribution is a function that distributes random variables in a graph that is shaped as a symmetrical bell. It does so by arranging the probability distribution for each value. Let’s use Python numpy for this.

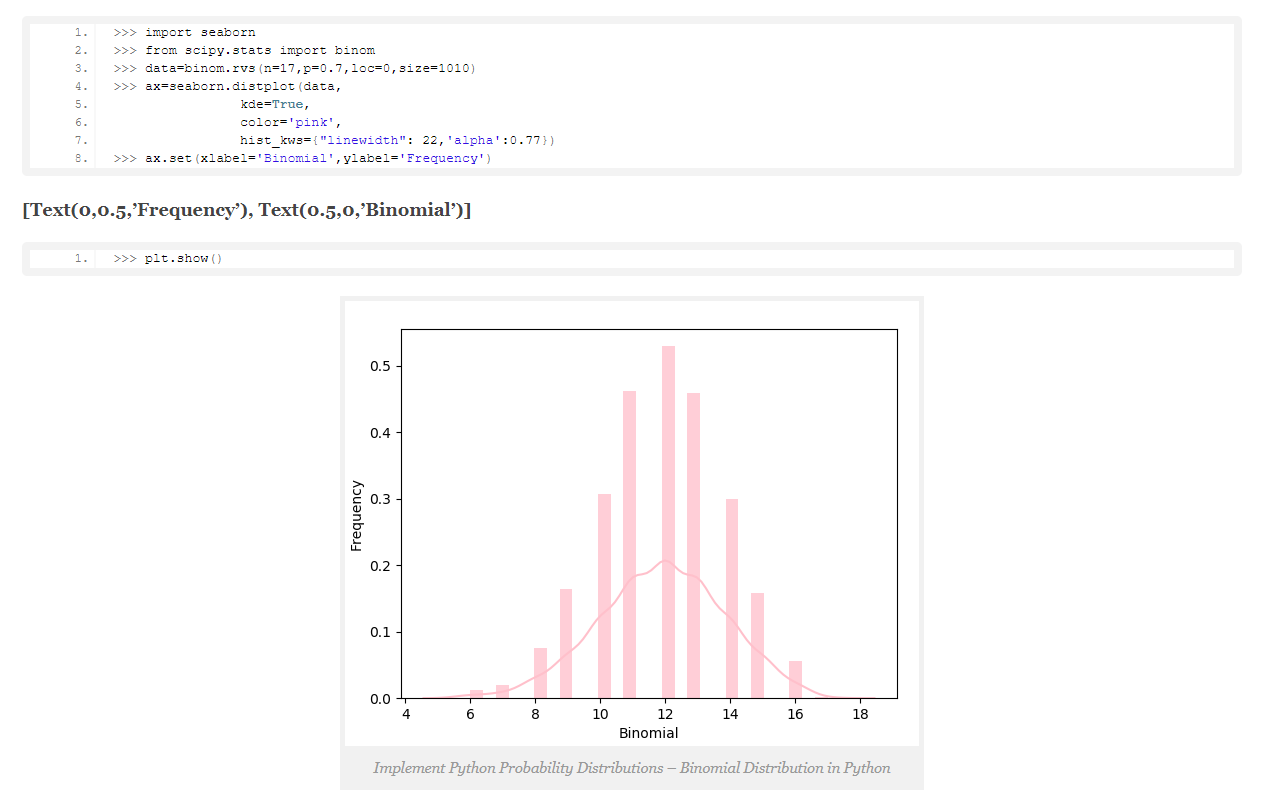
b. Binomial Distribution in Python:
Python binomial distribution tells us the probability of how often there will be a success in n independent experiments. Such experiments are yes-no questions. One example may be tossing a coin.
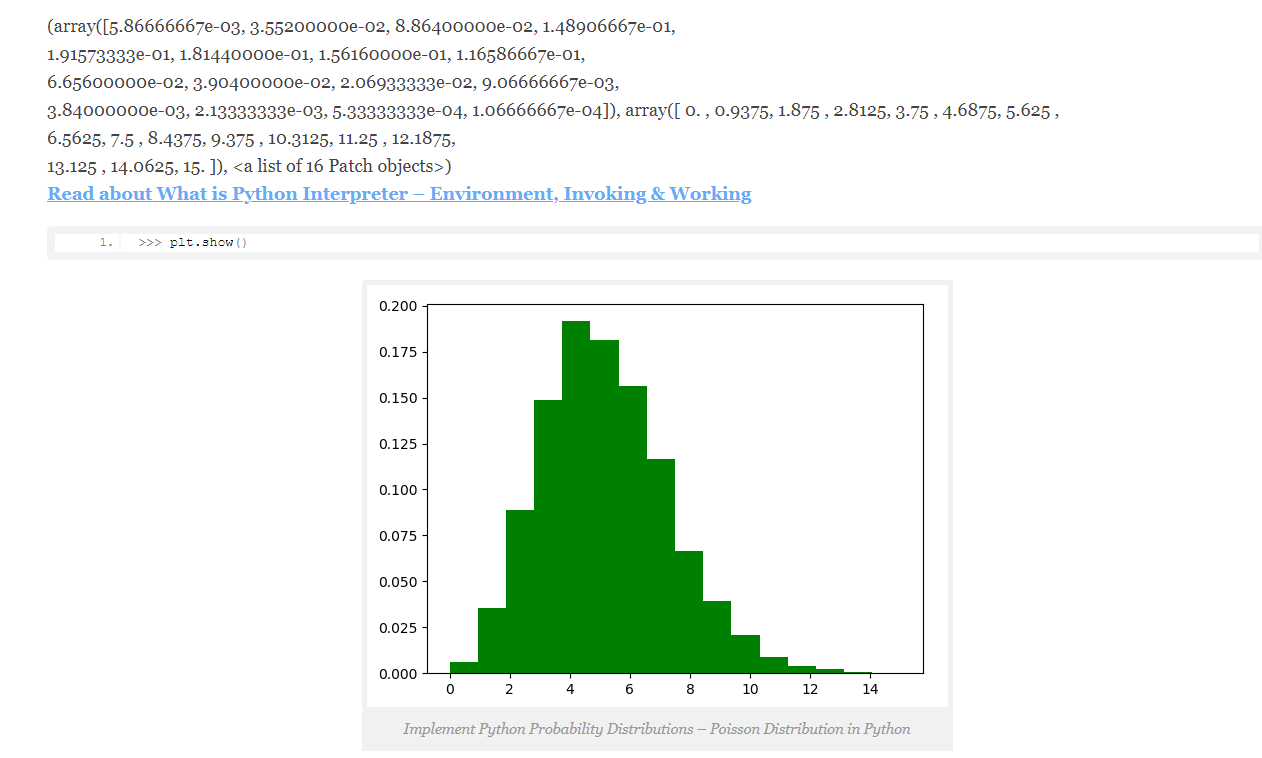
c. Poisson Distribution in Python:
Python Poisson distribution tells us about how probable it is that a certain number of events happen in a fixed interval of time or space. This assumes that these events happen at a constant rate and also independent of the last event.
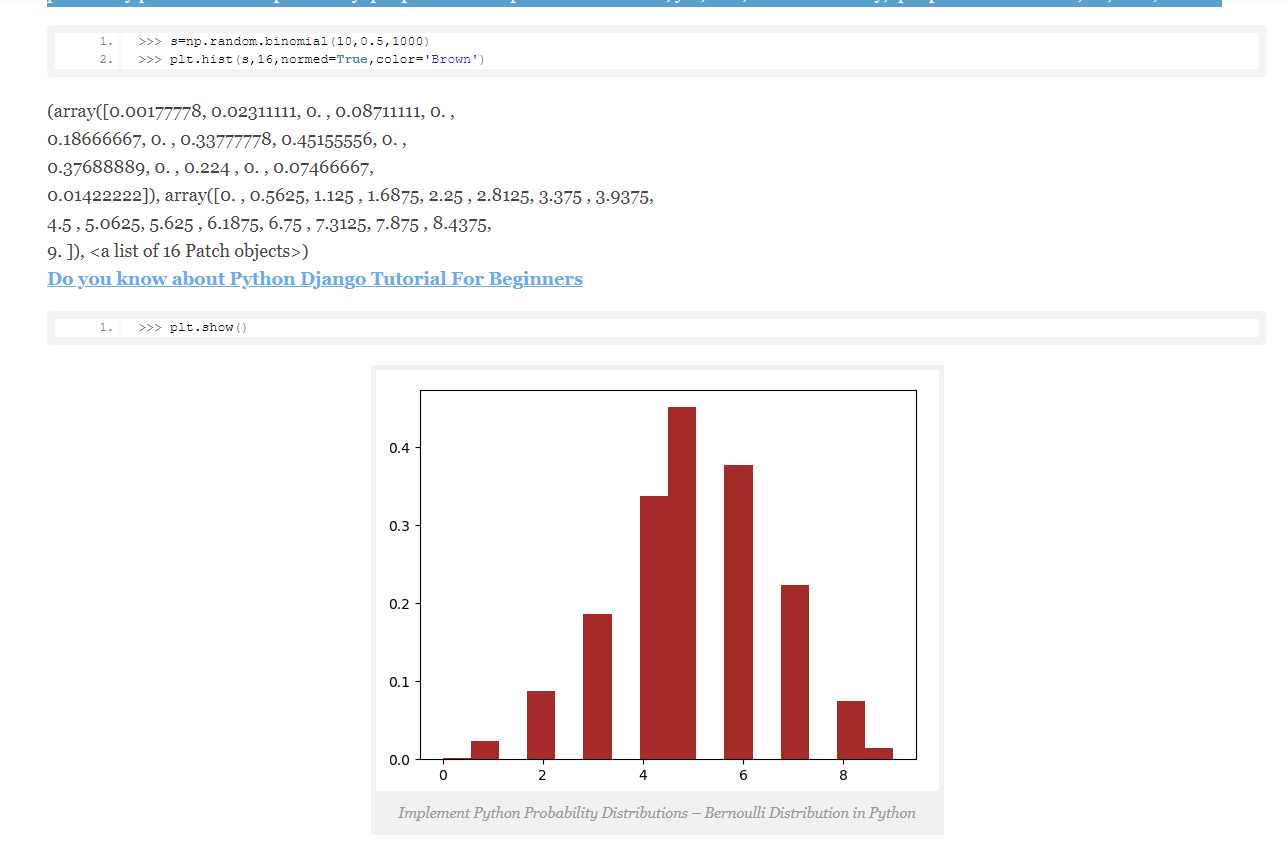
d. Bernoulli Distribution in Python
Python Bernoulli Distribution is a case of binomial distribution where we conduct a single experiment. This is a discrete probability distribution with probability p for value 1 and probability q=1-p for value 0. p can be for success, yes, true, or one. Similarly, q=1-p can be for failure, no, false, or zero.
4. Conclusion:
Hence, we studied Python Probability Distribution and its 4 types with an example. In addition, we learned how to implement these Python probability distributions.
by OBADA ALHAWJREH.*
My name is obada jaber, I’m 27 years old, I studied Mechanical engineering and i graduated from al balqa applied university, i am now a software student. OBADA ALHAWJREH.
Support or Contact:
Having trouble with Pages? Check out our : email or phone number : 0781912474 or contact support for gethub and we’ll help you sort it out. 🚑 🚑 🚑